EDUCATION
Pharma Tariffs: Impact Drug Costs and Global Healthcare
Pharma tariffs are a critical yet often overlooked factor influencing drug prices and accessibility worldwide. These import taxes on pharmaceuticals can significantly affect healthcare systems, patient affordability, and even the pace of medical innovation. With countries imposing varying tariff rates, the global pharmaceutical industry faces complex challenges in balancing cost, supply chain efficiency, and equitable access to medicines.
In this article, we’ll explore how pharma tariffs shape market dynamics, their economic implications, and potential strategies to mitigate their impact. Whether you’re a policymaker, healthcare professional, or concerned consumer, understanding these tariffs is essential to navigating today’s pharmaceutical landscape.
What Are Pharma Tariffs?
Pharma tariffs are taxes imposed on imported pharmaceutical products, including raw materials, finished drugs, and medical equipment. Governments use these tariffs to protect domestic industries, generate revenue, or regulate drug imports. However, they can also lead to higher drug prices, supply chain disruptions, and limited access to essential medications.
Types of Pharma Tariffs
-
Import Duties – Standard taxes applied to foreign pharmaceutical products.
-
Excise Taxes – Levied on specific drugs, often those deemed non-essential.
-
Countervailing Duties – Imposed to counteract foreign subsidies that distort market prices.
-
Retaliatory Tariffs – Enacted as trade war measures, affecting drug costs unpredictably.
The Economic Impact of Pharma Tariffs
Pharma tariffs influence drug affordability, particularly in developing nations where healthcare budgets are already strained. When import costs rise, pharmaceutical companies often pass these expenses onto consumers, leading to inflated retail prices. Additionally, tariffs can disrupt supply chains, delaying critical drug availability in emergencies.
Key Consequences
-
Higher Drug Prices – Tariffs increase production costs, ultimately burdening patients.
-
Reduced Competition – Domestic manufacturers may face less pressure to innovate if foreign competitors are taxed heavily.
-
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities – Over-reliance on tariff-free regions can create bottlenecks during crises.
Global Comparison of Pharma Tariffs
Different countries apply pharma tariffs based on economic policies and healthcare priorities. Below is a comparison of how five major economies approach these taxes:
| Feature | USA | EU | China | India | Brazil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Tariff Rate | 0-6% | 0-4% | 2-8% | 10-15% | 12-18% |
| Essential Drug Exemptions | Yes | Yes | Limited | No | Partial |
| Impact on Local Pharma | Moderate | Low | High | Very High | High |
| Supply Chain Efficiency | High | High | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Patient Affordability | Moderate | High | Low | Very Low | Low |
As seen, countries like India and Brazil impose higher tariffs to protect domestic industries, but this often results in costlier medications for patients. Conversely, the U.S. and EU maintain lower tariffs, ensuring smoother drug accessibility but potentially disadvantaging local manufacturers.
Strategies to Mitigate the Effects of Pharma Tariffs
While pharma tariffs are often politically driven, stakeholders can adopt strategies to lessen their negative impact:
1. Localized Manufacturing
Producing drugs domestically reduces reliance on imports, minimizing tariff exposure. Many nations now incentivize local pharmaceutical production through tax breaks and subsidies.
2. Trade Agreements
Bilateral or multilateral trade deals can lower or eliminate pharma tariffs, fostering smoother cross-border drug distribution.
3. Price Negotiations
Governments and healthcare providers can negotiate bulk pricing with manufacturers to offset tariff-induced cost hikes.
4. Stockpiling Critical Drugs
Maintaining strategic reserves of essential medicines ensures availability despite supply chain disruptions caused by tariffs.
The Future of Pharma Tariffs
As global trade tensions persist, pharma tariffs will remain a contentious issue. Policymakers must balance economic protectionism with public health needs, ensuring tariffs don’t compromise drug accessibility. Innovations like digital customs clearance and AI-driven supply chain optimization may also help mitigate tariff-related inefficiencies.
FAQs
1. How do pharma tariffs affect drug prices?
Pharma tariffs increase import costs, which pharmaceutical companies often pass on to consumers. This leads to higher retail prices, particularly in countries with steep tariff rates.
2. Which countries have the highest pharma tariffs?
Developing nations like India and Brazil impose higher tariffs (10-18%) to protect domestic industries, whereas the U.S. and EU maintain lower rates (0-6%).
3. Can pharma tariffs lead to drug shortages?
Yes, if tariffs make imports prohibitively expensive, supply chains may falter, causing delays or shortages in critical medications.
4. Are there exemptions for essential medicines?
Some countries, like the U.S. and EU, exempt life-saving drugs from tariffs, while others apply partial or no exemptions.
5. How can companies reduce tariff-related costs?
Strategies include shifting production locally, leveraging trade agreements, and negotiating bulk purchase discounts.
6. Will pharma tariffs decrease in the future?
This depends on global trade policies. While some nations may lower tariffs to improve drug access, others could increase them to boost domestic manufacturing.
EDUCATION
N-Gon Definition: What It Is and Why It Matters in Math and 3D Design
Understanding what an n-gon is can make a big difference—whether you’re solving geometry problems or refining a 3D model. In this guide, we break down the n-gon definition, its mathematical significance, and its role in fields like computer graphics and architectural modeling.
Let’s dive in.
What Is an N-Gon?
An n-gon is a geometric shape—specifically, a polygon—with n number of sides. The “n” is a variable that stands for any integer greater than or equal to 3.
- A triangle is a 3-gon.
- A square is a 4-gon.
- A pentagon is a 5-gon.
- …and so on.
So, an n-gon is simply a general term for any polygon with “n” sides.
In mathematics, the term helps describe polygons in a scalable way—without naming each shape individually.
Key Characteristics of an N-Gon
Whether regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular (uneven sides/angles), all n-gons share some basic properties.
Properties of an N-Gon
- Number of sides: Exactly n sides.
- Number of angles: n internal angles.
- Sum of interior angles: (n−2)×180∘(n – 2) \times 180^\circ
- Can be regular or irregular: Based on side and angle uniformity.
- Convex vs. concave: Determined by internal angle measures.
Mathematical Use of N-Gons
In pure mathematics and geometry education, n-gons serve as tools to teach:
- Angle calculation
- Symmetry principles
- Polygon classification
They’re also foundational in proofs and theorems, such as tessellations and tiling problems.
N-Gons in 3D Modeling and Game Development
In 3D modeling software like Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max, the term “n-gon” has a different context. It refers to any polygon with more than four sides—used in modeling complex surfaces.
Why N-Gons Matter in 3D Graphics
- Easier modeling: Useful during the sculpting phase.
- Potential rendering issues: N-gons may deform poorly when animated.
- Topology concerns: Many engines prefer tris (3-gons) or quads (4-gons) for cleaner results.
Game engines like Unity or Unreal often require meshes to be converted to tris for real-time rendering.
Real-World Applications of N-Gons
Architecture and CAD
Designers use n-gons in structural diagrams and floor plans to represent irregular walls and surfaces.
Data Visualization
N-gons are used in radial charts or custom graph plotting in advanced data interfaces.
Education and Research
Geometry classes often use n-gons to teach concepts of measurement, symmetry, and polygon classification.
Pros and Cons of Using N-Gons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Flexible in modeling complex shapes | Can create issues in animation |
| Reduce mesh density for organic forms | Not ideal for real-time rendering |
| Used in mathematical generalization | Harder to control in topology cleanup |
How to Work with N-Gons in Modeling
If you’re a 3D artist, here’s how to handle n-gons safely:
- Use during modeling, but convert to quads/tris before export.
- Clean up topology to avoid artifacts.
- Test animation deformations in rigged models.
Expert Opinions on N-Gons
Dr. Hannah Fry, mathematician and author, says:
“N-gons represent a beautiful simplicity in geometry—providing a formulaic way to understand complexity.”
Jonathan Williamson, Blender Foundation instructor:
“N-gons are great during early modeling stages, but clean quad-based topology is critical for professional-grade output.”
Dr. Michael Bailey, UC Davis Computer Graphics Professor:
“In real-time graphics, n-gons pose risks. Clean meshes with tris or quads are much more GPU-friendly.”
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Relying on n-gons in game assets
- Ignoring non-planar faces in modeling
- Forgetting to triangulate meshes before export
Final Thoughts
The n-gon might sound like a complex term, but it’s simply a flexible way of referring to any polygon with “n” sides. Whether you’re a math student, digital artist, or engineer, understanding n-gons can streamline your work and reduce errors.
Master the n-gon, and you master a foundation of geometry and modeling.
FAQ’s
What is the difference between a polygon and an n-gon?
A polygon is the general term; an n-gon is a more technical way of saying “a polygon with n sides.”
Are n-gons bad in 3D modeling?
Not inherently, but they can cause problems in animation or real-time rendering if not triangulated properly.
How do you find the sum of interior angles of an n-gon?
Use the formula: (n−2)×180∘(n – 2) \times 180^\circ
Can an n-gon be regular?
Yes, if all its sides and angles are equal, it’s called a regular n-gon.
What’s the smallest possible n-gon?
The triangle (3-gon) is the smallest polygon that forms a closed shape.
EDUCATION
Anna’s Archive: The People’s Open Library in a Digital Age

Anna’s Archive is a free, open-source shadow library that aggregates and mirrors books, academic papers, and digital content from multiple sources—especially those that are often locked behind paywalls. Emerging from the ethos of information freedom and preservation, it became particularly prominent after the legal takedown of Z-Library in late 2022.
It’s not just a pirate website—it’s an ambitious archiving project that aims to preserve humanity’s knowledge for future generations. For students, researchers, and digital seekers frustrated by inaccessible paywalled journals or expensive textbooks, Anna’s Archive serves as a gateway to content that might otherwise be lost or hidden.
Who Uses Anna’s Archive and Why?
Target users of Anna’s Archive include:
- Students and researchers in developing nations or underfunded institutions
- Independent scholars without institutional access to major databases
- Digital librarians and archivists looking to preserve cultural or scientific heritage
- Tech-savvy individuals who value online anonymity and open access
Whether you’re finishing your dissertation or chasing an obscure research topic, Anna’s Archive offers a treasure trove of scholarly, historical, and technical resources.
Key Features of Anna’s Archive
Comprehensive Content Indexing
Anna’s Archive aggregates and mirrors from:
- LibGen (Library Genesis)
- Sci-Hub (for academic journals)
- Z-Library (mirrored collections)
- Internet Archive (metadata and mirror support)
With over 25 million books and growing, it has become one of the most extensive open databases in the world.
Powerful Search Capabilities
Users can:
- Search by title, author, ISBN, or topic
- Access multiple mirror links
- View metadata (formats, file size, tags)
- Choose from PDF, ePub, MOBI, and other formats
Privacy-Centric Design
Anna’s Archive is designed to protect user identity, offering:
- No login requirement
- HTTPS encryption
- .onion access via Tor for anonymous browsing
- An actively updated mirror list in case domains are blocked
“Anonymity is a feature, not a flaw. Information wants to be free, and people deserve access to knowledge regardless of borders or bureaucracy.”
— Anna’s Archive Manifesto
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Anna’s Archive exists in a legal gray zone. While the project claims to preserve and democratize information, many publishers argue it facilitates copyright infringement.
According to Dr. Alexandra Elbakyan, founder of Sci-Hub:
“If knowledge is a human right, then the tools to access that knowledge must be accessible too.”
— Interview with Wired Magazine, 2023
Important: Users must understand the legal implications in their region. Some countries treat access to shadow libraries as illegal, while others are more lenient. Use tools like VPNs and Tor Browser cautiously and ethically.
How to Safely Use Anna’s Archive
If you decide to explore Anna’s Archive, here are some safety tips:
- Always use HTTPS or visit via Tor (.onion) address
- Don’t share personal info on any shadow library platforms
- Use VPNs to obscure your IP
- Avoid downloading executable files or anything suspicious
Anna’s Archive itself doesn’t host malware, but third-party mirrors might.
Why Anna’s Archive Matters in 2025
With rising digital censorship and academic gatekeeping, platforms like Anna’s Archive represent a counterculture movement for open access. They’re not just tools—they’re statements.
“We are in an age where digital preservation is activism. Anna’s Archive is our modern-day Library of Alexandria.”
— Dr. Carla Reyes, Digital Archivist at MIT
Alternatives and Complementary Resources
If you’re seeking legal or open-access platforms, consider:
- Internet Archive (https://archive.org) – Public domain books, historical media
- Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) – Peer-reviewed academic articles
- Open Library (https://openlibrary.org) – Borrow eBooks with a free account
- Project Gutenberg – Free eBooks, mostly classics in public domain
Anna’s Archive is best viewed as a supplement, not a replacement, for legal sources.
Final Thoughts
Anna’s Archive is more than a database—it’s a digital lifeline for millions worldwide. As academia grows more expensive and online information becomes increasingly gated, platforms like Anna’s Archive provide a radical alternative rooted in equity and preservation.
If you’re a privacy-conscious researcher or student navigating limited access, Anna’s Archive might just be the hidden gem you didn’t know you needed.
FAQ’s:
Is Anna’s Archive legal?
It depends on your country. While Anna’s Archive itself does not host content directly, it indexes and mirrors databases that are controversial and often banned.
Is it safe to use?
If accessed via HTTPS or Tor and used responsibly (no personal data, no executable files), it’s relatively safe. A good VPN is also recommended.
What types of content can I find?
- Textbooks
- Academic research
- Fiction and non-fiction
- Technical manuals
- Historical and cultural texts
Can I contribute to the archive?
Yes, through metadata corrections or hosting mirrors. Developers can also contribute to the open-source project via GitHub.
Is it available in multiple languages?
The site supports international searches, though most metadata and titles are in English.
EDUCATION
Understanding n-gon Geometry: A Beginner-Friendly Guide Understanding n-gon Geometry: A Beginner-Friendly Guide
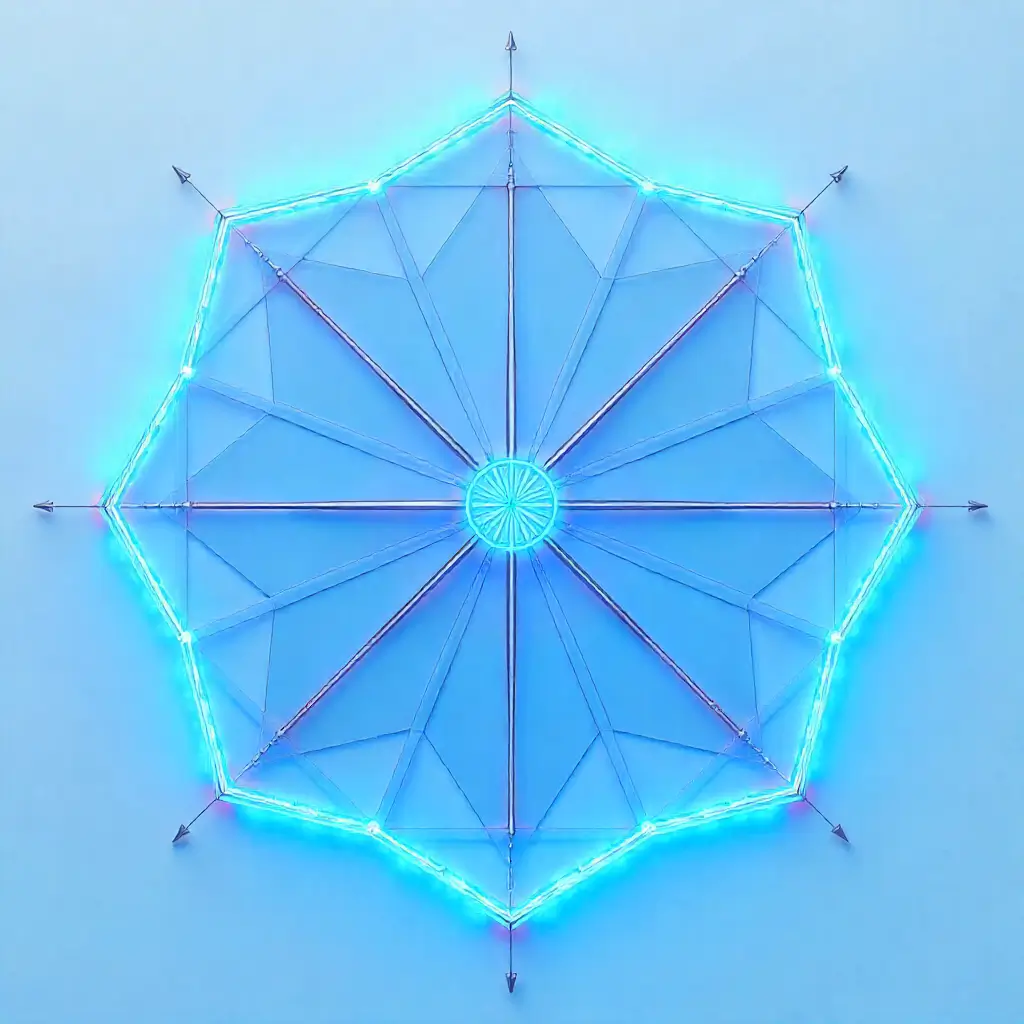

Geometry plays a crucial role in mathematics and real-world problem-solving. One concept that often puzzles students is the idea of the n-gon. Whether you’re preparing for a school exam, building a math project, or just curious about polygons, this guide breaks it down simply and clearly.
What Is an n-gon in Geometry?
An n-gon is a polygon with “n” sides, where “n” is any integer greater than or equal to 3. That means if a shape has 3 sides, it’s a 3-gon (triangle); if it has 8 sides, it’s an 8-gon (octagon), and so on.
Key Characteristics of an n-gon:
- It is a closed shape formed by straight line segments.
- The sides meet at vertices (corners).
- Each interior angle connects two sides.
- “n” can be any whole number ≥ 3.
Examples of Common n-gons:
| n | Name of Polygon | Shape Example |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | Triangle | ▲ |
| 4 | Quadrilateral | ■ |
| 5 | Pentagon | ⬟ |
| 6 | Hexagon | ⬢ |
| 8 | Octagon | ⬣ |
| 10 | Decagon | ⬡ |
How to Classify n-gons
n-gons can be classified based on side length, angle size, and symmetry.
Regular vs. Irregular n-gons
- Regular n-gon: All sides and angles are equal.
- Irregular n-gon: Sides and/or angles are not equal.
Convex vs. Concave n-gons
- Convex n-gon: All interior angles are less than 180°.
- Concave n-gon: At least one interior angle is greater than 180°.
Why Understanding n-gons Matters
Knowing how to identify and work with n-gons is foundational in:
- Geometry problems involving angles, perimeter, and area.
- Computer graphics and modeling (used in game design and animation).
- Architecture and engineering, where precise shapes are essential.
How to Calculate Interior Angles of an n-gon
One of the most useful properties of an n-gon is its interior angles.
Formula:
Sum of interior angles = (n – 2) × 180°
For a regular n-gon:
Each angle = [(n – 2) × 180°] / n
Example:
For a regular pentagon (n = 5):
- Sum = (5 – 2) × 180 = 540°
- Each interior angle = 540 / 5 = 108°
Real-World Applications of n-gons
Learning about n-gons isn’t just for math class. These shapes appear in:
- Architecture: Dome patterns and tile layouts
- Science: Molecular structures and atomic models
- Technology: Computer-aided design (CAD), 3D modeling, and game design
- Art: Mandalas, tessellations, and geometric painting styles
Expert Insights and References
“Polygons, especially regular n-gons, form the building blocks of geometric understanding. Their properties are widely used in both academic and applied settings.”
— Dr. Nancy L. DeVault, Professor of Mathematics, Mathematical Association of America (MAA)
“In computer graphics, regular n-gons are key in mesh generation and surface modeling.”
— Prof. David Mount, Computer Science Department, University of Maryland, CMSC 420 Geometry Lecture Series
“Understanding the sum of interior angles is foundational for students, and it builds essential logical reasoning skills.”
— Khan Academy Geometry Curriculum, Khan Academy
Final Thoughts
The concept of an n-gon might seem simple, but it holds tremendous importance in both math theory and real-life applications. Whether you’re solving geometry problems or designing complex patterns, mastering n-gons gives you a strong foundation in spatial reasoning and logical thinking.
Keep practicing. The more shapes you explore, the more patterns you’ll recognize!
EXPLORE MORE
FAQ,s
What is the minimum value of “n” for an n-gon?
Answer: The smallest polygon has 3 sides, so n = 3 (a triangle).
Can an n-gon have curved sides?
Answer: No, by definition, polygons (and therefore n-gons) must have straight sides.
Is a circle an n-gon?
Answer: A circle is not an n-gon because it has no straight sides or vertices. However, a polygon with a very large “n” (e.g., 1000-gon) can approximate a circle visually.
How do I construct a regular n-gon?
Answer: Use a protractor and compass for precise angle division. In software like GeoGebra or CAD tools, you can generate them with just a few clicks.
What is the use of learning about n-gons?
Answer: Besides exams and tests, understanding n-gons helps with problem-solving in design, engineering, programming, and more.
-

 TECH5 months ago
TECH5 months agoOnionPlay Safe to Use in 2025? | Safer Alternatives, Privacy Tips & VPN Picks
-
 TECH5 months ago
TECH5 months agoDooflix App for PC: Best Ways to Use It on Windows 10/11
-
 TECH5 months ago
TECH5 months agoIs Scrolller Safe? A 2025 Guide to NSFW Browsing with Confidence
-

 BLOG6 months ago
BLOG6 months agoMedihoney: The Natural Healing Power Revolutionizing Wound Care
-

 TECH5 months ago
TECH5 months agoIs F95 Safe? A Complete 2025 Guide for Privacy-Conscious NSFW Gamers
-

 BUSINESS6 months ago
BUSINESS6 months agoBloomberg Billionaires Index: Unveiling the Wealthiest Lives
-
 BUSINESS6 months ago
BUSINESS6 months agoHuns Yellow Pages: The Ultimate Business Directory for Local Searches
-

 EDUCATION5 months ago
EDUCATION5 months agoAnna’s Archive: The People’s Open Library in a Digital Age
